- Stefania Milione
- Review
Suspect Moschcowitz syndrome: how, when, why
- 1/2019-Febbraio
- ISSN 2532-1285
- https://doi.org/10.23832/ITJEM.2019.012
Rosario Bottone1, Stefania Milione1, Barbara Guerrera2, Mauro Giordano1
1. Department of Medical, Surgical, Neurological, Metabolic and Geriatric Sciences, University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli”, Naples, Italy
2. Internal Medicine, Clinical Hospital of Marcianise, ASL Caserta, Caserta, Italy
Abstract
Keywords
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia, thrombotic events, multiorgan damage, plasmapheresis.
Introduction
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) is an acute syndrome characterized by the presence of microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia and thrombocytopenia.
The first case of TTP was described by Moschowitz in 1924 [1]. Recently, between 1982 and 2001, several authors [2-5] identified in the deficiency of the metalloproteinase ADAMTS13 the primary pathogenic cause. TTP is a rare disease [6-8]. it occurs between 30 and 50 years of age, more frequently in the female sex. In the absence of treatment, mortality exceeds 90%, while it is reduced to 10-20% after adequate plasma plasmapheresis or infusion therapy. However, half the deaths are attributable to complications associated with plasmapheresis and hospitalization (sepsis, haemorrhages, thrombosis, etc.) [9]
Case Report
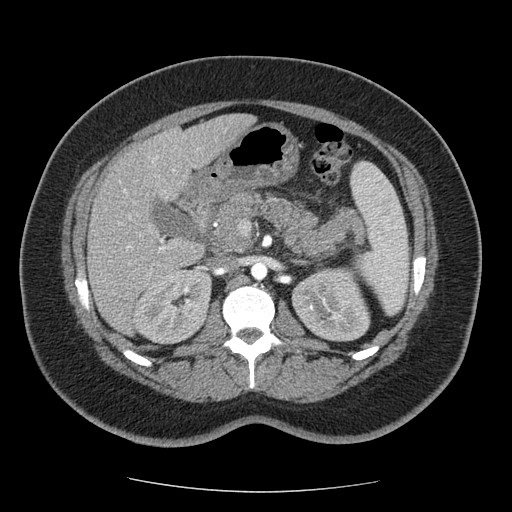
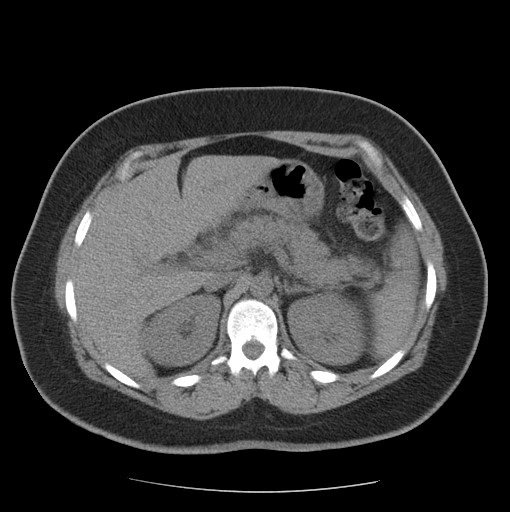
A 36-year-old italian woman came to our observation in the emergency department for abdominal pain, menometrorrhagia and vomiting. The patient had no significant past medical history. She had no significant clinical changes. She was hemodynamically stable.
Figure 1
Discussion
Conclusions
Our case report demonstrates the importance of the rapidity in setting the diagnosis and the treatment of PTT.
Therapy greatly reduces patient mortality. So far, the treatment performed by more physicians is not valid and nonconforming to the guidelines. Platelet transfusions are still administered by many increasing the risk of precipitating further thrombotic events. Their use is contra-indicated in TTP, unless there is life-threatening haemorrhage.
The symptomatology is often nonspecific and the diagnosis is posed with the presence of both microangiopathic hemolytic anaemia and thrombocytopenia. Multi-organ involvement, with the onset of acute pancreatitis, may be present.
However, symptoms demonstrating a multi-organ pathological involvement may be an expression of iatrogenic damage.
References
- Moschowitz E. Hyaline thrombosis of the terminal arterioles and capillaries: a hitherto undescribed disease. Proc N Y Pathol Soc1924;24:21-4.
- Moake JL, Rudy CK, Troll JH, et al. Unusually large plasma factorVIII:von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 1982;307:1432-5.
- Furlan M, Robles R, La¨mmle B. Partial purification and characterizationof a protease from human plasma cleaving von Willebrand factor to fragments produced by in vivo proteolysis.Blood 1996;87:4223-34.
- Tsai HM. Physiologic cleavage of von Willebrand factor by aplasma protease is dependent on its conformation and requires calcium ion. Blood 1996;87:4235-44.
- Levy GG, Nichols WC, Lian EC, et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature 2001;413:488-94.
- Scully M, Yarranton H, Liesner R, et al. (2008) Regional UK TTP registry: correlation with laboratory ADAMTS 13 analysis and clinical features. British Journal of Haematology,142, 819-826.
- Miller DP, Kaye JA, Shea K, et al. Incidence of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome. Epidemiology 2004;15:208-15.
- Schech SD, Brinker A, Shatin D, Burgess M. New-onset and idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: incidence, diagnostic validity, and potential risk factors. Am J Hematol 2006;81:657-63.
- George JN. The thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndromes: evaluation, management, and long-term outcomes experience of the Oklahoma TTP-HUS Registry, 1989-2007. Kidney Int Suppl 2009;112:S52-4
- Tsai HM, Rice L, Sarode R, Chow TW, Moake JL. Antibody inhibitors to von Willebrand factor metalloproteinase and increased binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets in ticlopidine-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Intern Med 2000;132:794-9.
- Miller RF, Scully M, Cohen H, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopaenic purpura in HIV-infected patients. Int J STD AIDS 2005;16:538-42.
- George JN. Clinical practice. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 2006;354:1927—35.
- Galbusera M, Noris M, Remuzzi G. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura–then and now. Semin in Thromb and Hemost, 2006; 32, 81–89.
- McDonald V, Laffan M, Benjamin S, Bevan D, Machin S, Scully MA. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura precipitated by acute pancreatitis: a report of seven cases from a regional UK TTP registry. Br J Haematol; 2009;144, 430–433.
- Burns ER, Lou Y, Pathak A. Morphologic diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol 2004;75:18-21.
- George JN. How I treat patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2000;96:1223-9.
- Szczepiorkowski ZM, Bandarenko N, Kim HC, et al., American Society for Apheresis; Apheresis Applications Committee of the American Society for Apheresis. Guidelines on the use of therapeutic apheresis in clinical practice: evidence-based approach from the Apheresis Applications Committee of the American Society for Apheresis. J Clin Apher 2007;22:106-75.
- Rock GA, Shumak KH, Buskard NA, et al. Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Study Group. N Engl J Med 1991;325:393-7.
- Allford SL, Hunt BJ, Rose P, Machin SJ, Haemostasis and Thrombosis Task Force, British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of the thrombotic microangiopathic haemolytic anaemias. Br J Haematol 2003;120:556-73.
- Scully M, Cohen H, Cavenagh J, et al. Remission in acute refractory and relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura following rituximab is associated with a reduction in IgG antibodies to ADAMTS-13. Br J Haematol 2007;136:451-61.
- Heidel F, Lipka DB, von Auer C, Huber C, Scharrer I, Hess G. Addition of rituximab to standard therapy improves response rate and progression-free survival in relapsed or refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. Thromb Haemost 2007;97:228-33.
- Foley SR, Webert K, Arnold DM, et al., Members of the Canada Apheresis Group (CAG). A Canadian phase II study evaluating the efficacy of rituximab in the management of patients with relapsed/refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Kidney Int Suppl 2009;112:S55-8.
- Moake JL, Rudy CK, Troll JH, et al. Unusually large plasma factor VIII:von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 1982;307: 1432-5.