- Maria Viviana Carlino
- Brief Report and Case Report
A mediastinal lymphoma detected by point-of-care ultrasound in a woman with worsening dyspnea. Hodgkin's Lymphoma: a case report
- 1/2018-Febbraio
- ISSN 2532-1285
- https://doi.org/10.23832/ITJEM.2018.002
Maria Viviana Carlino3 MD, Alfonso Sforza1 MD, Andrea d’Amato2 MD, Antonio Pagano1 MD, Mario Guarino3 MD, Costantino Mancusi2 MD, Fiorella Paladino1 MD
Abstract
A young woman presented to the Emergency Department with progressive dyspnoea. Point-of-care ultrasound, with pocket size device, was done upon arrival in Emergency Department. Thoracic ultrasound revealed a large left anterior mediastinal mass with significant left pleural effusion and left lower lobe atelectasis. Biopsy diagnosis was: Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Case Presentation
A 34-year-old woman presented to the Emergency Department (ED) with progressive dyspnoea. At the time of admission blood pressure was 120/70 mmHg, heart rate (HR) 70 bpm, regular, oxygen saturation was 95% (FiO2 21%) and respiratory rate was 22 breaths/min. Chest auscultation revealed abolished vesicular murmur at the left lung base. Cardiovascular examination revealed a normal cardiac rhythm, no murmurs, normal peripheral pulses and no oedema. The ECG showed sinus rhythm with normal AV conduction, normal axis and QT interval. Arterial blood gas analysis on room air revealed mild respiratory alkalosis with mild metabolic alkalosis, reduced partial pressure of oxygen (72 mm Hg), normal hemoglobin, electrolytes and lactate levels.
Results of blood tests showed a normal white blood cell count (7.600 cells per mm3), with renal and liver function test and serum electrolytes within the reference limits.
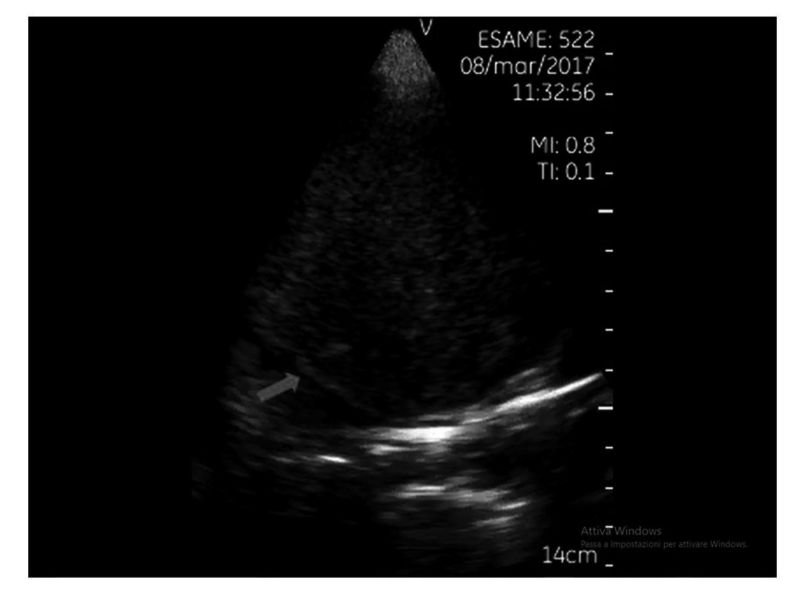
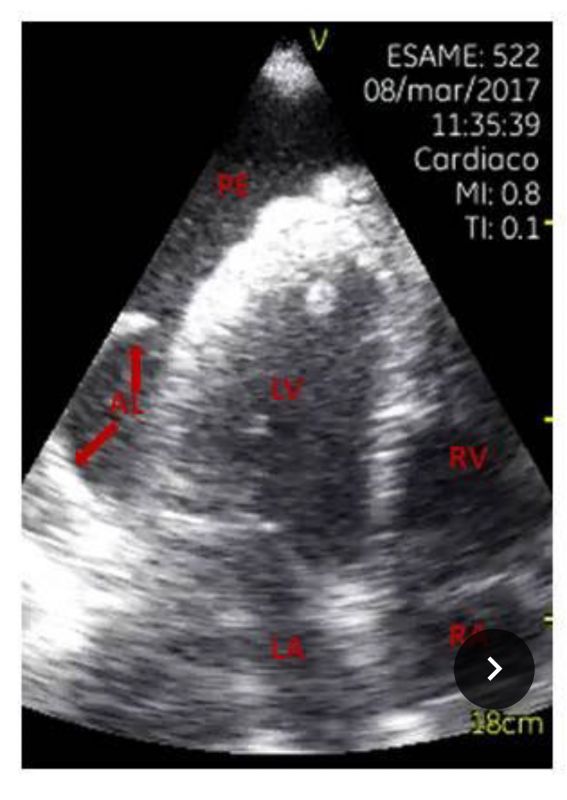
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS), with pocket size device, was done upon arrival in ED. Focused cardiac ultrasonography (FoCUS) showed normal left and right ventricular size and function. Thoracic ultrasound revealed a large left mediastinal mass (Figure 1, Video 1) with significant left pleural effusion and left lower lobe atelectasis (Figure 2, Video 2).
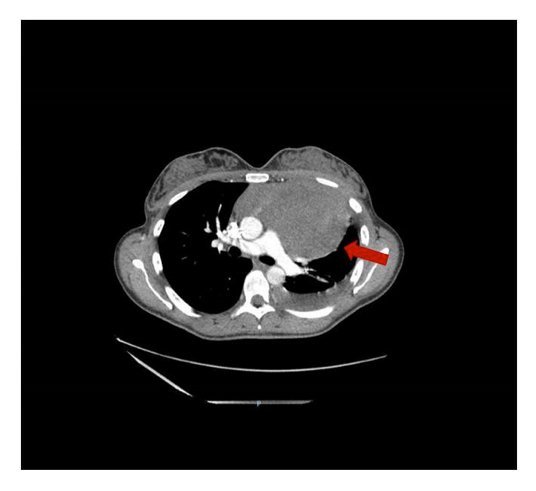
The patient underwent Contrast-enhanced CT scan of thorax that showed a large left anterior mediastinal mass (14.5×13.5×9.5 cm) suggestive of primary mediastinal lymphoma (Figure 3) and left significant pleural effusion with lingua and lower lobe atelectasis.
Mass biopsy confirmed the diagnosis: Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL).
Figure 1.Thoracic ultrasound (Parasternal approach): detection of a large left anterior mediastinal mass
Figure 3. Contrast-enhanced CT scan: evidence of a large left anterior mediastinal mass.
Discussion
References
-
Hodgkin lymphoma: 2016 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. SM., Ansell. Am J Hematol. 2016 Jun;91(4):434-42.
-
Pleural effusions in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma: clinical predictors and associations with outcome. Hunter BD, Dhakal S, Voci S, Goldstein NP, Constine LS. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014 Aug;55(8):1822-6.
-
Transthoracic US of the chest: clinical uses and applications. Koh DM, Burke S, Davies N, Padley SP. Radiographics. 2002 Jan-Feb;22(1):e1.
-
Diagnostic performance of multi-organ ultrasound with pocket-sized device in the management of acute dyspnea. Sforza A, Mancusi C, Carlino MV, et al. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017 Jun 19;15(1):16.